
Fully Convolutional Networks for Dense Water Flow Intensity Prediction in Swedish Catchment Areas
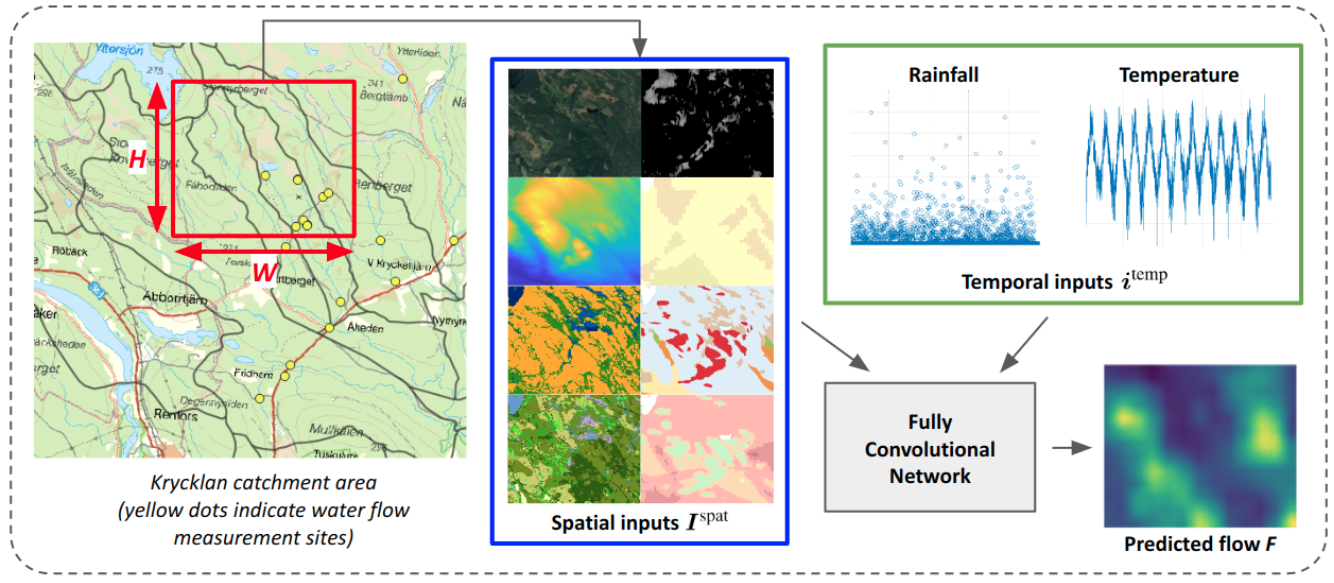
Intensifying climate change will lead to more extreme weather events, including heavy rainfall and drought. Accurate stream flow prediction models which are adaptable and robust to new circumstances in a changing climate will be an important source of information for decisions on climate adaptation efforts, especially regarding mitigation of the risks of and damages associated with flooding. In this work we propose a machine learning-based approach for predicting water flow intensities in inland watercourses based on the physical characteristics of the catchment areas, obtained from geospatial data (including elevation and soil maps, as well as satellite imagery), in addition to temporal information about past rainfall quantities and temperature variations. We target the one-day-ahead regime, where a fully convolutional neural network model receives spatio-temporal inputs and predicts the water flow intensity in every coordinate of the spatial input for the subsequent day. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to tackle the task of dense water flow intensity prediction; earlier works have considered predicting flow intensities at a sparse set of locations at a time. An extensive set of model evaluations and ablations are performed, which empirically justify our various design choices. Code and preprocessed data have been made publicly available at this https URL.
Aleksis Pirinen, Olof Mogren, Mårten Västerdal
35th Annual Workshop of the Swedish Artificial Intelligence Society SAIS
PDF Fulltext
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3384/ecp199002
arxiv: 2304.01658
bibtex.